尼玛但增 (主编) 《罗布林卡珍藏文物辑选》 中国藏学出版社, 2011.
A Newar-copied pramāṇa manuscript? You don’t see those every day—especially in Nepal.

It’s not every day that philology determines the future of a superpower. November 12, 2000 CE, was just such a day. The outcome of the 54th United States presedential election hung in the balance, awaiting a manual recount of the Florida ballots. Officials were shown on television holding up punched ballots to the light, straining to determine whether their chads were dimpled or pregnant, or had hanging or swinging doors.
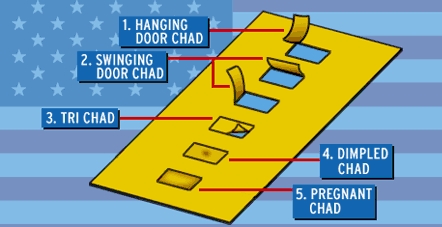
The officials’ process engendered doubt – doubt that could grow into a grey area which, left unchecked, might obscure entitlement and privilege itself. At this crucial juncture, former Secretary of State James Baker laid down his nation-changing methodological critique:
“How do you divine the intent of the voter on that voting card … with those little punch holes?” he said today on NBC’s Meet the Press. “You’re divining the intent of the voter with respect to whether it has two chads hanging down or whether it’s punched or whether it has an indentation? I mean, that’s crazy.” *
Textual critics were dismissed as diviners; textual criticism became an act of madness. The rest is history. But since history, especially bad history, loves nothing more than to repeat itself, the eve of the 57th presidential election provides an occasion to reflect on the value of philology.
Continue reading “Philology as national security threat”
Cecile Bründlmayer. Ethnography of the Kumbheśvara temple compound in Lalitpur (Patan), Nepal. Architecture, Iconography and Interaction within a sacred Landscape. Diplomarbeit, Universität Wien, 2011. 149 pp. [official site / PDF]

Anne Taylor Mocko. Demoting Vishnu: Ritual, politics, and the unmaking of Nepal’s monarchy. PhD diss., University of Chicago, 2012. 517 pp. UMI Number 3517176.
Chandrasekhar, Chaya. Pāla-Period Buddha Images: their hands, hand gestures, and hand-held attributes. PhD Dissertation, Ohio State University, 2004. xvi+375 pp. [official site / PDF (779.3 MB)]
This study identifies and classifies the Buddha images of the Pāla period (ca. eighth-twelfth centuries) of eastern India and Bangladesh. Specifically, the study examines the number of hands—whether a single pair or multiple pairs—hand gestures, and hand-held attributes of the Buddha images, and analyzes these elements in relation to the essential teachings of Mahāyāna and Vajrayāna Buddhism. […]
About 963 Buddha images among the known Pāla artistic corpus serve as the primary documents for the study.
Lee, Eun-Su. On defining Buddhist art in Bengal: the Dhaka region. PhD Dissertation, University of Texas at Austin, May 2009. 498 pp. [official site / PDF (224.3 MB)]
This dissertation addresses the significance of regional developments in Indian art, focusing on the Buddhist art tradition of the Dhaka region in East Bengal from approximately the seventh to twelfth century CE.

Johnson, Dennis. ‘Refuting the conditioned: the Saṃskṛtārthapratiṣedha of Candrakīrti’s Catuḥśatakaṭīkā’. Diplomarbeit, Universität Wien (Philologisch-Kulturwissenschaftliche Fakultät), 2012. [official / PDF]
The original Sanskrit text of CŚṬ is available only in form of fragments that cover about one third of the work, and there is a critical edition of these, based on a single manuscript (Suzuki 1994). A complete Tibetan translation by Sūkṣmajñāna and Nyi ma grags is contained in the bsTan ‘gyur (P. vol. 96, 5266 ya 33b4-273b6; D. ya 30b6-239a7; C. ya 29a6-236a7; N. ya 34b2-246a6).Furthermore, there is an English translation of the verse text (Lang 1986), but not of the commentary, for which there are but translations of single chapters into different languages (Lang 1976 and 2003; Tillemans 1990 are the English ones).
The thesis further contributes to this work by presenting a translation and summary of the hitherto unaddressed chapter of CŚṬ XV, on the basis of the remaining Sanskrit text (in this case CŚṬ XV.18-25) and a critical edition of the Tibetan translation.
Anshuman Pandey. ‘Proposal to Encode the Siddham Script in ISO/IEC 10646’.
ISO/IEC JTC1/SC2/WG2 N4294 L2/12-234R. PDF. 2012/08/01.
Mr. Pandey’s proposal – now no longer preliminary – promises to fill yet another gaping hole in the standard encoding of important Indic scripts. Now would be an appropriate time to comment, if you haven’t already commented.
(I would hope, at minimum, for the addition of a full set of ten digits in the final proposal. Often such basics fall through the gaps because the corpus of readily available primary material is so limited. Here‘s a nice “7-8th century” bilingual manuscript with a varṇamālā (no digits, though) which is both in good condition and readable online, thanks to the care of its Japanese custodians. Incidentally, this clearly confirms that two of the “Punctuation and ornaments” in Pandey’s Fig. 33 are ornamental final anusvāra [अं字].)
Comments should be emailed to Anshuman Pandey, whose address is given in the N4294 proposal (link above) and at the bottom of his personal website (link).

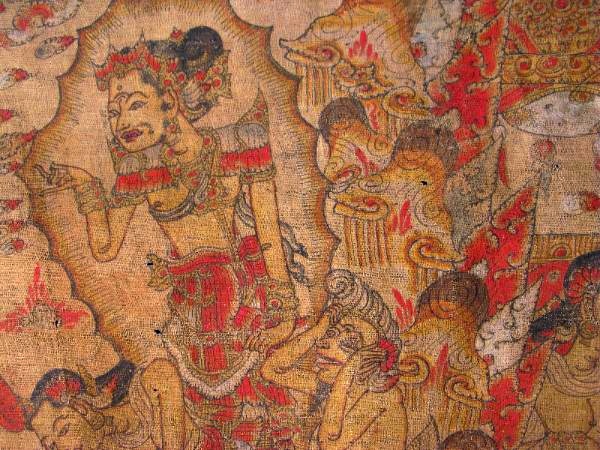
Fletcher, Margaret; Hunter, Th.; Supomo; Worsley, Peter. Sumanasāntaka – Death by a Sumanasa Flower: An Old Javanese Epic Poem, Its Indian Source and Balinese Illustrations. KITLV Press: January 2013. 1,000pp. USD$125.00. ISBN: 978-90-6718-394-9. [distributed in the United States by UH Press].
“This five-part study of a previously unpublished Old Javanese Kakawin contributes to the history of a narrative that had its origins on the Indian subcontinent and was reworked in the form of epic poems and paintings in Java and Bali.”
