Oliver von Criegern. ‘Das Sarvadharmaguṇavyūharājasūtra: ein Mahāyānasūtra zum Buchkult aus den Gilgitfunden’. München Univ., Diss., 2009. 237 pp. [unseen]
Li, ‘Candrakīrti’s Āgama’ (2012)
Li, Shenghai 李勝海 [academia.edu]. ‘Candrakīrti’s Āgama: A Study of the Concept and Uses of Scripture in Classical Indian Buddhism’. PhD diss., University of Madison-Wisconsin, 2012. 311 pp.
From the Abstract
This dissertation examines scripture as a concept and the various roles that authoritative Buddhist texts play as such in the intellectual history of Buddhism. While it considers what Buddhist authors explicitly speak about scripture, the project brings into focus the recorded uses of authoritative texts, with an interest in discovering intellectual practices and learning about the management and transmission of knowledge. The main source materials of this study consist of instances of scriptural references found in the scholastic and commentarial works of several influential Indian and Tibetan authors, all of whom are connected with the pivotal figure of Candrakīrti (ca. 570-640), whose major writings lie at the center of the investigation. […]
Highlighting a keen awareness of the problem of reifying reason displayed by certain Buddhist writers from the Madhyamaka School of thought, the dissertation argues more specifically that the Buddhist scholastic tradition is cognizant of the hermeneutical condition of understanding and of reason’s contingency upon language, context, and tradition.
Lin, ‘The Wish-Fulfilling Vine in Tibet’ (2011)
Nancy Grace Lin. ‘Adapting the Buddha’s Biographies: A Cultural History of the Wish-Fulfilling Vine in Tibet, Seventeenth to Eighteenth Centuries’. PhD diss., University of California at Berkeley, 2011. 319 pp. ISBN 9781267228482, ProQuest ID 928450843.
From the Abstract
The Wish-Fulfilling Vine of Bodhisattva Avadānas (Skt. Bodhisattvāvadānakalpalatā, Tb. Byang chub sems dpa’i rtogs pa brjod pa dpag bsam gyi ’khri shing) by Kṣemendra is an eleventh-century Sanskrit anthology of stories about the previous existences of the Buddha and his disciples, along with events from the Buddha’s final life. Translated into Tibetan circa 1270 and incorporated into the Tibetan Buddhist canon, by the seventeenth century the Vine occupied a place of high prestige in Tibet. I argue that adaptations of the Vine—condensed literary digests, paintings, and woodcuts—constitute sophisticated forms of commentary that reveal the ingenuity and concerns of their producers. […]
In Chapter One I trace how the Fifth Dalai Lama (1617-1682) and his court popularized the Vine through public instruction, paintings, and literary activities. These conspicuously cultured displays promoted renewed interest in Sanskrit and the Indic origins of Buddhism, while contributing to broader projects of knowledge production and state-building. In Chapter Two I demonstrate how the lay Pho lha dynasty (r. 1728-1750) appropriated the Vine, sponsoring two large-scale multimedia productions while developing models for lay kingship and patronage. In Chapter Three I argue that Si tu Paṇ chen Chos kyi ’byung gnas (1700-1774), an influential monk of Sde dge in eastern Tibet, articulated his vision of the ideal monastic through the design of Vine paintings and other literary and visual productions on the Buddha’s life. In Chapter Four I study Zhu chen Tshul khrims rin chen (1697-1774), court chaplain of Sde dge, and his work on the Vine as commentaries on cultural production.

Huang, ‘Sanskrit-Chinese collated Laṅkāvatāra’ (2011)
 Someone please tell me that this isn’t simply the CBETA e-text pasted alongside the DSBC e-text, printed out and slapped between a cover? Even priced at 88 Yuan (currently less than USD$14), that would be still worth less than the paper it’s printed on:
Someone please tell me that this isn’t simply the CBETA e-text pasted alongside the DSBC e-text, printed out and slapped between a cover? Even priced at 88 Yuan (currently less than USD$14), that would be still worth less than the paper it’s printed on:
黄宝生(译注/作者) 《梵汉对勘入楞伽经》 中国社会科学出版社 ISBN 9787500496267 88.00元 600千字
Huang, Baosheng. Fàn-Hàn duì kān Rù léngjiā jīng [Sanskrit-Chinese* collation of the Laṅkāvatāra-sūtra]. Beijing: China Social Sciences Press, 2011. 765 pp. [official site]
* The “Tang-era translation” (唐代譯).
The same publisher has put out a similar treatment of the Bodhicaryāvatāra, apparently. STOP PRESS: and the Vimalakīrtinirdeśa (I guess they are using GRETIL’s ‘unofficial’ e-text).
Continue reading “Huang, ‘Sanskrit-Chinese collated Laṅkāvatāra’ (2011)”
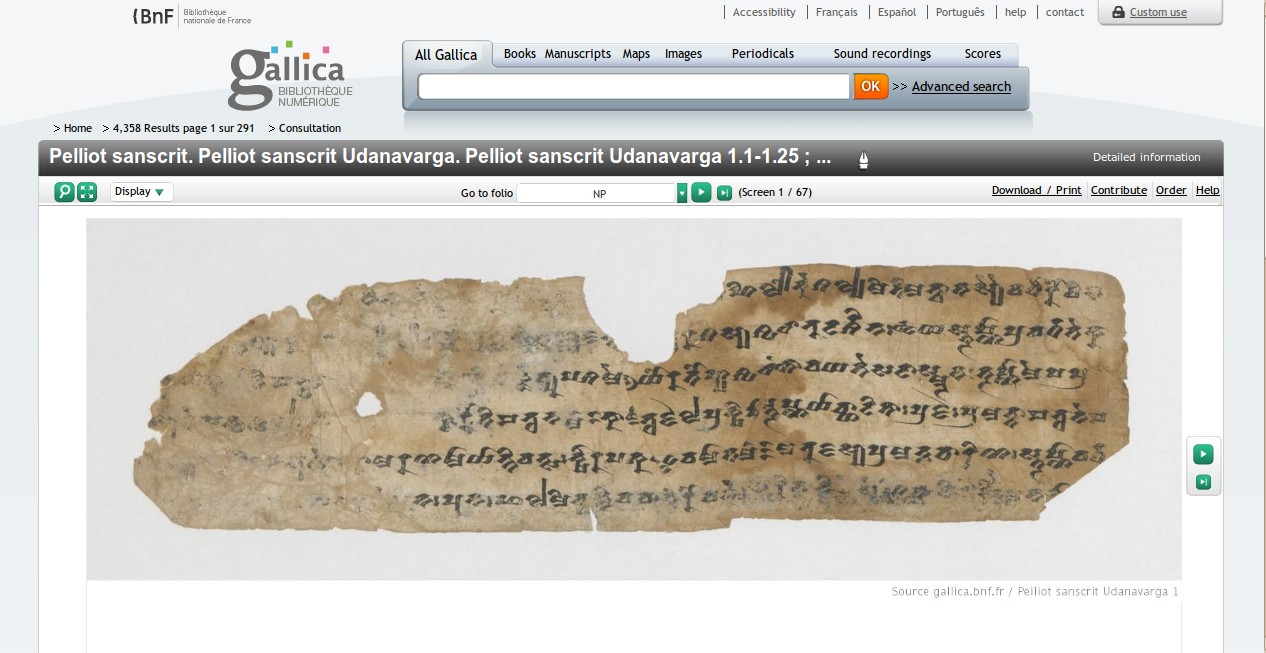
BnF Pelliot sanscrit MSS online
In glorious detail:
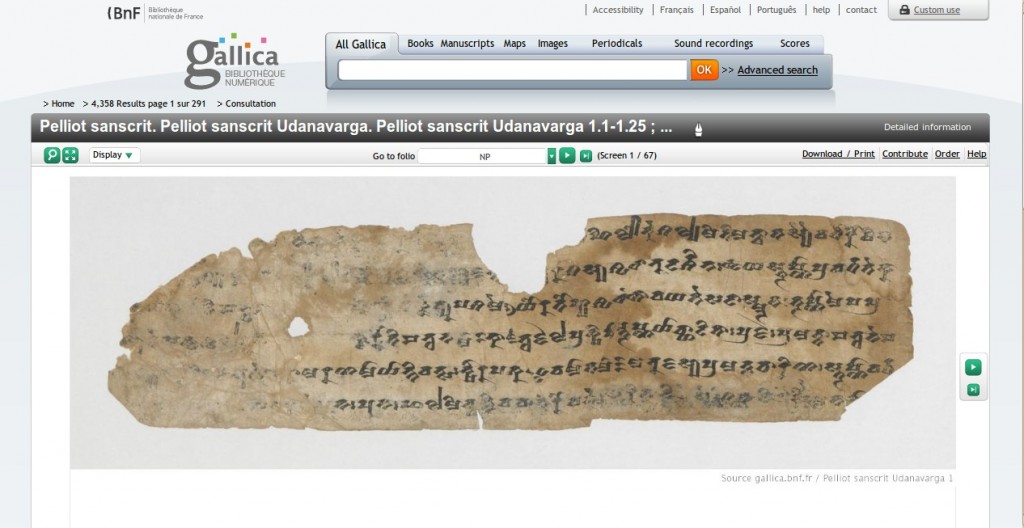
With Japan and Europe now putting significant parts their manuscript holdings online — with only beneficial consequences, it seems — let us hope that our friends in China rapidly follow suit.
Link: http://gallica.bnf.fr/
Oldmeadow, ‘Rimé: Buddhism without prejudice’ (2012)
Peter Oldmeadow. Rimé: Buddhism without prejudice. Carlton North: Shogam Publications [facebook], 2012 [forthcoming]. ISBN 9780980502220.
Buddhism without prejudice? That would be the Sanskritic tradition, surely.
But as Dr. Oldmeadow informs me: “I’ve attempted to bring together available material on the Rime movement and its context and present it in an accessible fashion which, hopefully, also throws some light on present-day Tibetan Buddhism.”
Fontein, ‘The Gaṇḍavyūha reliefs of Borobudur’ (2012)
Jan Fontein. Entering the Dharmadhātu: A study of the Gaṇḍavyūha reliefs of Borobudur. Studies in Asian Art and Archaeology 26. Leiden, Boston: Brill, 2012. ~240 pp. ISBN-13: 978-9004211223. €125. [official site]
From the Abstract
 Entering the Dharmadhātu compares the complete set of panels with three early Chinese translations of Central Asian and Indian Sanskrit manuscripts of the Gaṇḍavyūha. This first identification of the entire series in English concludes with a discussion of the new perspectives on the meaning, symbolism, and architecture of Borobudur that a reading of the Gaṇḍavyūha suggests.
Entering the Dharmadhātu compares the complete set of panels with three early Chinese translations of Central Asian and Indian Sanskrit manuscripts of the Gaṇḍavyūha. This first identification of the entire series in English concludes with a discussion of the new perspectives on the meaning, symbolism, and architecture of Borobudur that a reading of the Gaṇḍavyūha suggests.
Jonathan Silk
Jonathan Silk not only studies Mahāyāna Buddhism; he thinks about it as well. Is that unusual? Put it this way: I feel that I can recommend his work on that basis alone.
- A number of Prof. Silk’s articles are available at the University of Leiden’s online repository.
- For starters: timely thoughts on Buddhist studies in his Oratie, Lies, Slander and the Study of Buddhism, delivered April 1st, 2008 (but no laughing matter). Offering so much to discuss, I present just this excerpt:
I would be a happy man had I a nickel — that’s a small denomination American coin – for every time I have been told that Buddhism is not a religion, but rather a philosophy, a way of life. This is more than a rhetorical strategy by which an interested Westerner allows himself to explore Buddhism without feeling an apostate for doing so. For it derives its validity only by denying Buddhist traditions their intrinsic identity, and Buddhists — traditional, Asian Buddhists — their autonomy. Once one denies that Buddhism is a religion, it ceases to be an integral part of anyone’s life. Buddhism becomes something optional, adventitious, incidental even to the people whose lives it structures. For Westerners disaffected with religion, this may be a happy solution. But at least for the scholar, it is an impossibility, for it constitutes a refusal to acknowledge the tradition in its multiplicity and complexity, or even in its most intrinsic nature. [2008:12]
- Official Site: http://www.leidenuniv.nl/professoren/show_en.php3-medewerker_id=950.htm
Liland, ‘The transmission of the Bodhicaryāvatāra’ (2009)
Fredrik Liland. ‘The transmission of the Bodhicaryāvatāra: The history, diffusion, and influence of a Mahāyāna Buddhist text’. M.A. thesis, Universitetet i Oslo, 2009. [official site/PDF] Supervised by Jens E. Braarvig.
From the Abstract
The thesis is concerned with the 7th Century Mahāyāna Buddhist text Bodhicaryāvatāra (BCA) and its significance as a vehicle for cultural exchange. We trace its history in India and beyond, from its proposed author Śāntideva’s hand, its contemporary influence in India, and its impact in the lands—Nepal, Tibet, China, Mongolia, and beyond—and languages—Sanskrit, Newari, Tibetan, Chinese, Mongolian, and others—where it travelled. The nature of its influence has varied with the times and places where it has found itself, but in all instances it received a prominent place of canonical status, and was mostly revered.
[…]
The BCA has received quite a lot of attention in modern scholarship since the first publication of a critical Sanskrit edition by Minayev in 1889. A large number of new manuscripts of the text have surfaced since then, and a separate chapter is dedicated to philological concerns and the dire need for a new and updated version that will take into account also the new knowledge we now have of the text[‘]s history. A mostly unnoticed commentary, the Bodhicaryāvatāra-ṭippaṇi, also receives i[t]s long overdue attention in this chapter.
Liland’s thesis presents a long over due bibliographically-oriented update to scholarship on the Bodhicaryāvatāra. Two other scholars are said to have been recently working on a critical edition of the text: Daniel Stender and Richard Mahoney. I do not know whether either are proceeding.
One stand-out feature of Liland’s thesis is the attention it pays to Nepalese sources and translations in the Newar (“Newari”) language, which, as regular readers know, are routinely neglected in Buddhist studies, notwithstanding the fact that they originate in direct contact with the Sanskrit original in a South Asian Buddhist setting. Despite this unusual but welcome development, I can point to at least three areas of further improvement:
- “Ratna Bahādur Vajrācārya (1893-1955), of whom not much is known” (p.92): in fact, at least four (mostly short) biographies of this outstanding figure are in print, including a dedicated and independently published treatment by Manish Shakya.
- No mention of (the many) translations into South Asian vernaculars; here’s one in Nepali. Not all such translations were done from Sanskrit, but some have been.
- No reference to manuscripts in private or recently documented collections.
Continue reading “Liland, ‘The transmission of the Bodhicaryāvatāra’ (2009)”
Sciberras, ‘Buddhist Philosophy & Environmentalism’ (2010)
Sciberras, Colette. ‘Buddhist Philosophy and the Ideals of Environmentalism’. Doctoral thesis, Durham University, 2010. [official site / PDF.]
From the Abstract
I argue that the teachings found in the Pāli canon cannot easily be reconciled with a belief in the intrinsic value of life, whether human or otherwise. This is because all existence is regarded as inherently unsatisfactory, and all beings are seen as impermanent and insubstantial, while the ultimate spiritual goal is often viewed, in early Buddhism, as involving a deep renunciation of the world.
Therefore, the discussion focuses mostly on the Mahāyāna, which, I suggest has better resources for environmentalism because enlightenment and the ordinary world are not conceived as antithetical. Continue reading “Sciberras, ‘Buddhist Philosophy & Environmentalism’ (2010)”